Difference Between Gravitation and Weightlessness
Difference Between Gravitation and Weightlessness
Gravitation
Definition: Gravitation, or gravity, is the force by which a planet or other body draws objects toward its center. It is a fundamental force of nature that causes objects with mass to be attracted to one another.
Characteristics:
- Universal Force: Gravity acts on all objects with mass, no matter how big or small.
- Dependence on Mass and Distance: The strength of gravitational force between two objects depends on their masses and the distance between them. The force is stronger with larger masses and shorter distances.
- Equation: Newton’s law of universal gravitation describes it mathematically as:
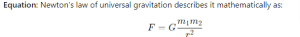
Effects:
- Keeps celestial bodies in orbit (e.g., Earth around the Sun, Moon around Earth).
- Causes objects to fall towards the ground when dropped.
- Influences tides due to the gravitational pull of the moon.
- Shapes the formation and structure of planets, stars, and galaxies.
Weightlessness
Definition: Weightlessness, or zero gravity, is the sensation or condition experienced when there is no net gravitational force acting on a body. This typically happens when an object is in free fall or in orbit, creating the illusion of no gravity.
Characteristics:
- Free Fall Condition: An object in free fall under the influence of gravity alone (e.g., an astronaut in orbit around Earth) experiences weightlessness because it is accelerating at the same rate as gravity.
- Lack of Normal Force: Weightlessness occurs because there is no contact force (normal force) pushing back against the object. For example, astronauts in orbit do not feel their weight because both they and their spacecraft are falling towards Earth at the same rate.
- Microgravity Environment: In orbit, objects experience microgravity, where the gravitational force is very small but not completely absent.
Effects:
- Causes objects and people to float as if there is no gravity.
- Affects bodily functions such as blood circulation, muscle mass, and bone density due to the lack of gravitational force.
- Used in scientific experiments to study the effects of gravity and simulate conditions of space.
Summary
- A universal force that attracts objects with mass toward each other.
- Described by Newton’s law of universal gravitation.
- Responsible for the motion of planets, falling objects, and tidal forces.
Weightlessness:
- A condition experienced when there is no net gravitational force felt.
- Occurs in free fall or orbit, creating the sensation of zero gravity.
- Results in floating objects and altered physical conditions due to the absence of normal force.
Difference Between Gravitation and Weightlessness
Related Topics:
Effects of Weightlessness






