Most Common Medical terms in medicine| Nursing
Most Common Medical terms in medicine| Nursing
Medical terms in medicine are specialized vocabulary used by healthcare professionals to accurately describe the human body, its conditions, procedures, and treatments. These terms are often derived from Latin and Greek roots, which allow for precision and consistency across different languages and regions. Here are some examples of medical terms across various categories: Most Common Medical terms in medicine| Nursing
Anatomy:
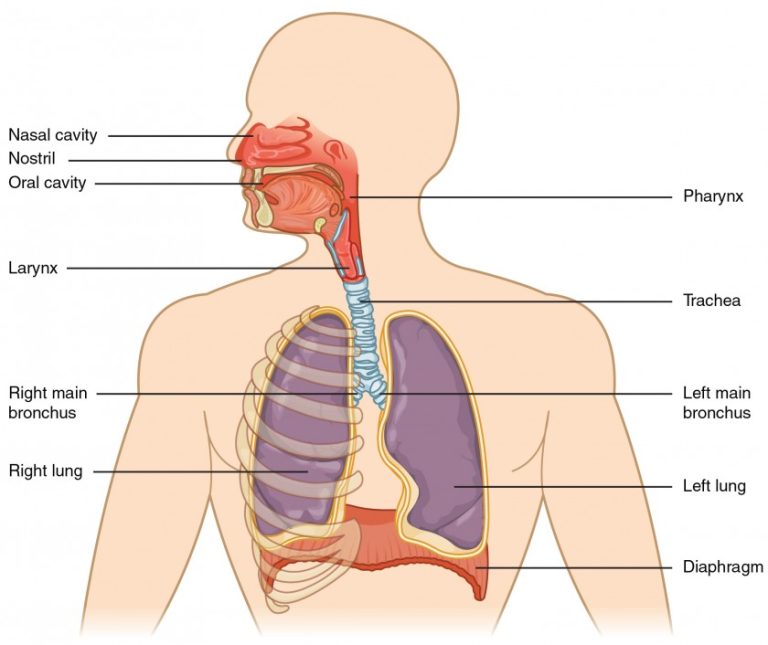
Anatomy is the identification and description of the structures of living things. It is a branch of biology and medicine
- Cardi – Heart (e.g., Cardiology: the study of the heart)
- Gastro – Stomach (e.g., Gastroenterology: the study of the stomach and intestines)
- Hepato – Liver (e.g., Hepatitis: inflammation of the liver)
- Neuro – Nerve (e.g., Neurology: the study of the nervous system)
- Osteo – Bone (e.g., Osteoporosis: a condition characterized by weak bones)
Conditions
- -itis – Inflammation (e.g., Arthritis: inflammation of the joints)
- -oma – Tumor (e.g., Carcinoma: a type of cancerous tumor)
- -pathy – Disease (e.g., Neuropathy: disease of the nerves)
- -emia – Blood condition (e.g., Anemia: a condition with a lack of healthy red blood cells)
- -algia – Pain (e.g., Neuralgia: nerve pain)
Procedures
- -ectomy – Surgical removal (e.g., Appendectomy: surgical removal of the appendix)
- -scopy – Visual examination (e.g., Endoscopy: visual examination inside the body using an endoscope)
- -plasty – Surgical repair (e.g., Rhinoplasty: surgical repair of the nose)
- -graphy – Recording or imaging (e.g., Angiography: imaging of blood vessels)
- -therapy – Treatment (e.g., Chemotherapy: treatment with chemicals, typically for cancer)
Diagnostic Terms
- Hyper- – Excessive or high (e.g., Hypertension: high blood pressure)
- Hypo- – Deficient or low (e.g., Hypoglycemia: low blood sugar)
- Brady- – Slow (e.g., Bradycardia: slow heart rate)
- Tachy- – Fast (e.g., Tachycardia: fast heart rate)
- Dys- – Abnormal or difficult (e.g., Dysphagia: difficulty swallowing)
Treatment and Drugs
- Antibiotics – Drugs that kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria (e.g., Penicillin)
- Analgesics – Drugs that relieve pain (e.g., Ibuprofen)
- Antipyretics – Drugs that reduce fever (e.g., Acetaminophen)
- Antihistamines – Drugs that relieve allergic symptoms (e.g., Loratadine)
- Diuretics – Drugs that increase urine output (e.g., Furosemide)
General Medical Terms
- Acute – Sudden onset, short duration (e.g., Acute bronchitis)
- Chronic – Long-lasting, persistent (e.g., Chronic back pain)
- Benign – Non-cancerous (e.g., Benign tumor)
- Malignant – Cancerous (e.g., Malignant melanoma)
- Prognosis – The expected outcome of a disease (e.g., Good prognosis)
Understanding these terms helps healthcare professionals communicate accurately and efficiently, ensuring clear understanding and effective patient care.